Home / Single Post
Take your digital marketing to the next level with data-driven strategies and innovative solutions. Let’s create something amazing together!
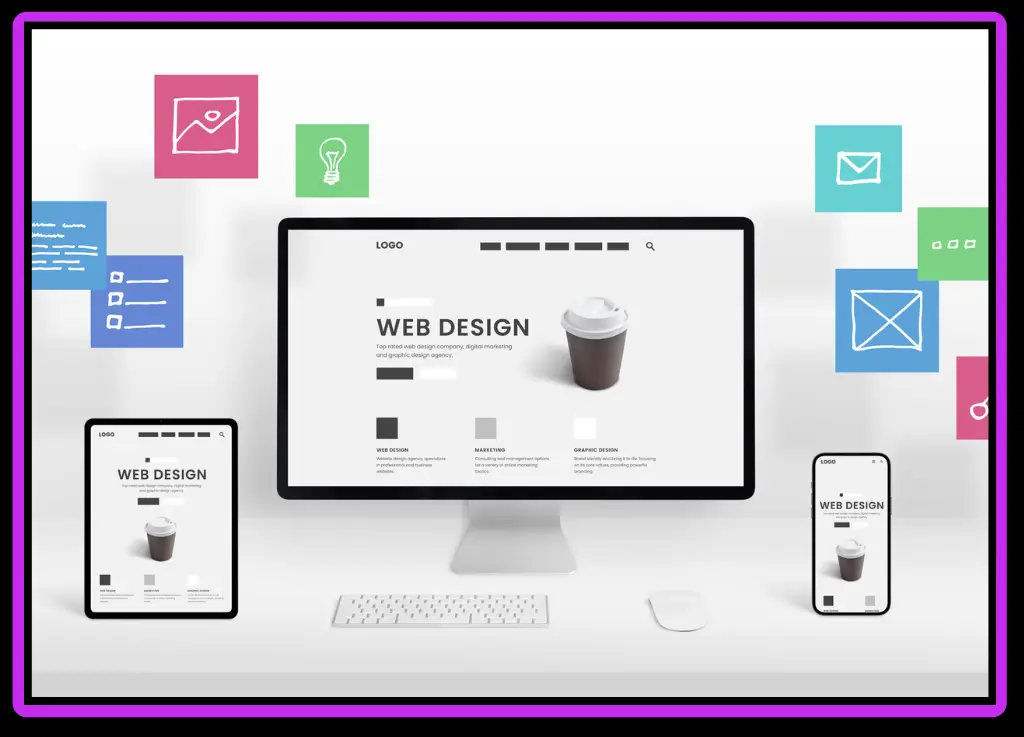
Internet access has changed fundamentally. Desktop computers were the main gateways to the digital universe a decade ago. We browse now on laptops and tablets, smartwatches, and most commonly, mobile phones. The explosion of screens and resolutions on each device, with their own sizes and resolutions, presented a challenge to web designers and developers. How can you make sure a website functions and looks great on screens as small as a playing card and as large as televisions? Responsive web design is the answer.
This guide gives a complete overview of responsive web development (RWD). We will examine its origins, core principles, and tangible benefits for businesses and users. From flexible grids to viewport meta tags, you will learn the techniques and tools needed to create responsive sites. We will discuss common problems and solutions, show examples of RWD that are exceptional, and look to the future of web design. You will learn why RWD has become a necessity for any online presence.
It’s important to understand the predecessors of responsive design. Websites were designed with fixed layouts in the early days of the internet. Designers built pages with fixed pixel widths that were optimized for desktop monitor resolutions at the time. The approach was successful when all devices were similar, but with the introduction of the iPhone in 2007, the paradigm shifted dramatically.
A growing number of people were suddenly accessing the internet on handheld devices with small screens. Sites with fixed widths were unusable on these devices. The text was too small for reading, and the images were a mess. Users had to pan and zoom constantly to navigate. Initial solutions included creating separate mobile-specific websites that were often hosted under a subdomain such as ” m.website.com”. Adaptive design is a technique that serves a different site depending on the device that was detected. It was an improvement, but it was also inefficient. The two codebases required double the work for updating and managing content.
Ethan Marcotte, a web designer from New York City, coined the term ” responsive web design in a groundbreaking article published by A List Apart in 2010. He suggested a fluid and more efficient solution: one website that can adapt its layout to any screen size. He advocated a flexible grid-based design combined with media queries, fluid images, and instead of creating multiple fixed-width designs. This idea paved the way for the modern web by offering a unified approach to a fragmented device landscape.
Three fundamental principles are the foundation of responsive web design. These principles, when combined, allow a website to offer an optimal viewing experience on a wide range of devices.
Fluid grids are the foundation of RWD. Responsive design does not use fixed pixels for elements such as columns and containers. Instead, it uses relative units. If a layout contains two columns, for example, you could set each column to occupy 50% rather than 500 pixels. The layout elements will scale proportionally to the changes in screen size. This principle is demonstrated when you resize the browser window. The content flows gracefully to fill the space available.
All visual media, just like the grid layout, must be flexible. Images with fixed dimensions can break fluid layouts by expanding beyond the boundaries of their containers on smaller screens. CSS can be used to scale images within their container elements. One common technique is applying max-width 100% to images. The image will display in its original size when viewed on large screens, but it will be reduced to fit the container of smaller devices. This prevents horizontal scrolling while maintaining the integrity and layout.
The “magic” of RWD is media queries. These are CSS3 features that allow you to apply styles depending on the characteristics of the device being used. The characteristics are the screen resolution and orientation of the device (portrait vs. landscape), as well as the height and width of the viewport.
Designers use media queries to define “breakpoints”-specific viewport widths at which the layout should change. A three-column desktop layout might change to a two-column layout on a tablet, and a one-column mobile layout. Media queries allow designers to create customized experiences by targeting different screen sizes.
It’s not just about aesthetics. Responsive web design has measurable, significant benefits for business.
A responsive website is built using a combination of specific HTML and CSS technologies. The web designer’s job is to implement the most important tools.
Include the viewport meta tag as the first step. This tag tells the browser how to control the page’s dimensions and scaling. This tag instructs the browser on how to control page dimensions and scaling. It is necessary because mobile browsers would render the page using a desktop width, and then scale it down to produce tiny, unreadable text.
This is how the standard viewport tag appears:
This code instructs the browser that the viewport width should match the width of the device screen and to use a 1:1 scaling when the first page is loaded.
Many designers use CSS frameworks to speed up the development process. These frameworks come with an integrated responsive grid system, as well as pre-styled elements. These frameworks do most of the work for you when creating responsive layouts. Popular choices include:
The importance of readability cannot be overstated. Text is also responsively designed. Text can be scaled to fit the screen by using relative units such as em, rem, or the more recent viewport units (vw and vh). It ensures that body text and headlines are readable and proportioned across all devices.
RWD is used by many leading websites. Their responsiveness is evident when you resize the browser window.
Responsive design principles are here to remain, but technology is constantly evolving. The new CSS features Flexbox and Grid make it easier to create dynamic and complex layouts that are responsive. These new layout modules offer more intuitive and powerful ways to control elements’ alignment, spacing, and order.
The concept of “intrinsic Web Design” is also gaining popularity. This approach focuses primarily on creating responsive components, which adapt to their container and not just the browser viewport. This allows for modular and reusable design systems. The need for flexible and content-aware designs will continue to grow as devices diversify, from foldable phones to AR Glasses.
It’s more than just a technical solution; responsive web design is a philosophy that puts the user first. It recognizes that users are going to access content at their own pace, using the device of their choice. You can ensure that all visitors have a positive experience by creating a flexible, responsive web presence. It is easier to develop, improves SEO, and respects user context. The evolution of the web from rigid layouts to fluid interfaces is reflected in this journey.
It is a method of developing websites that automatically adapts the layout and content to any screen size. This approach uses a single codebase and URL. This provides a consistent user experience and eliminates separate mobile sites. Focus is on adapting to all devices.
Three main components are fluid grids, images that can be resized, and media queries. Fluid grids can be sized by percentage, while flexible images are scaled to fit their container. Media queries can also change styles based on screen size.
It’s a fantastic tool for Search Engine Optimization. Google prefers responsive sites because they provide a better user experience. One URL for every device simplifies indexing and scanning, which helps to prevent duplicate content and improve rankings.
This list is not set in stone, but it does include: a fluid menu for navigation, a dynamic one (like hamburger menus on mobile), and interactive elements that are scalable. Together, these elements create a responsive website.
At ZadSpark Technologies, we are the designers of digital success. Since 2021, our agency based in the UAE and UK has been creating outstanding solutions that help brands transform into market leaders. Just like a lighthouse guiding ships away from stormy waters and the uncertainty of the deep sea, ZadSpark Technologies empowers businesses in the UK and around the world to find growth, creativity, and endless opportunities.
User Admin
We fix slow websites, weak SEO, poor apps, and Failing digital Strategies